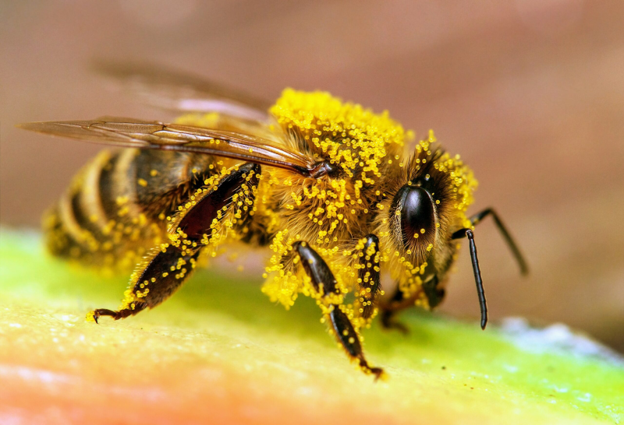
The gentle hum of bees going about their work in a field of flowers might seem like a small, ordinary part of our world, but don’t be fooled by their seemingly unassuming presence. Honeybees, often overlooked and taken for granted, are nothing short of miraculous creatures that play a vital role in our ecosystem. Not only are they the diligent producers of that sweet elixir we all love – honey, but they are also the unsung heroes responsible for pollinating countless plants, including many of the fruits and vegetables we rely on for sustenance.

Honeybees are the ultimate pollinators. As they collect nectar from flowers, they transfer pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part, allowing plants to produce fruits and seeds. This crucial service impacts our food supply significantly, as over 75% of the world’s leading food crops depend on pollinators, primarily honeybees, to some extent. Imagine a world without bees; it would be a world with far fewer apples, strawberries, almonds, and cucumbers, to name just a few.
While pollination is their primary role, honeybees also gift us with one of nature’s most delightful creations – honey. Bees transform nectar into honey by a fascinating process involving regurgitation and evaporation. The sweet golden substance is not only delicious but also boasts antibacterial properties and can be stored indefinitely. It’s a remarkable product of nature that we often take for granted.
Despite their incredible value, honeybees are facing a grave challenge – a significant decline in population. From 2022 to 2023, the US beekeepers lost 48.2% of the honey bee colonies. So what destroys such beautiful creatures? Let’s explore this list:
- Pesticides: The use of neonicotinoid pesticides in agriculture has been linked to bee deaths. These chemicals disrupt the bees’ ability to forage, navigate, and even reproduce.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agricultural expansion have led to a reduction in the availability of wildflowers and other essential plants for honeybees.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns and temperature extremes can affect bee behavior, disrupt plant flowering schedules, and impact their foraging efficiency.

Parasites and Diseases: Bees also face threats from mites and pathogens, which can weaken or kill entire colonies.
The decline in honeybee populations doesn’t only affect honey production and our ability to enjoy the fruits of their labor. It has far-reaching consequences. Reduced bee populations mean decreased pollination, which, in turn, can lead to lower crop yields and reduced food availability. In 2022, Honey Production in Canada Decreased by a Volume of 15.6%. This has implications for food security and the global economy.
In conclusion, honeybees are not just insects; they are life-givers. They provide us with food, sweet honey, and essential pollination services. It’s our responsibility to protect and preserve these incredible creatures. The decline in honeybee populations should serve as a wake-up call, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all life on our planet and the urgent need to protect and nurture the beings that sustain our world.
Interesting facts about bees:
– A single bee weighs 0.00025 pounds. 4,000 bees together weigh only one pound.
– A single bee can produce 1 tablespoon of honey in its lifetime.
– Bees can fly up to 19,3121 km/h.
– Bees communicate by dancing! Moreover, with its dance, each bee can tell about good nectar, warn about danger and even ask another bee to give it a massage!
– Bees can “rob” honey from other bees if honey from another hive is available (say, if a hive is open), or if times are lean.

Sources & Recommended Reading:
1) https://worldanimalfoundation.org/advocate/bee-statistics/
2) https://bigislandbees.com/blogs/bee-blog/14137357-bee-dances
3) https://bigislandbees.com/blogs/bee-blog/14137349-interesting-bee-honey-facts
4) https://extension.usu.edu/pests/factsheets/factors-contributing-to-bee-decline-PR.pdf